Creating User Identities¶
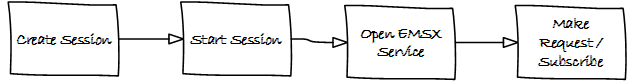
The steps involved in connecting to the EMSX API on the desktop are as follows:-
In the server environment, the user identities must be created and cached prior to the making requests. Therefore, the process would look as follows:-
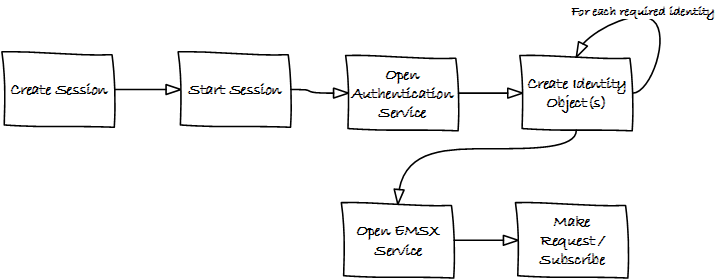
Note
Note: The EMSX API Server code samples demonstrate how to create identity object.
The first new step is to open the authentication service. This is done in the same way as for any other service in the Bloomberg API. For example:-
d_authsvc = "//blp/apiauth";
session.openServiceAsync(d_authsvc);
Once the service is opened, we need to create and send an authorization request. To create an identity for a specific user, you will need the AuthID for the user. This is the name the user is known by in the EMRS system for your server. The values for these names will have been agreed with you as part of the implementation of the server, or subsequently when adding a new user. Also, an IP address is required. The only requirement for this IP address is that it is unique amongst all the identities generated for a session. You can create and send the request as follows:-
private Identity userIdentity;
*
*
*
Service authService = session.getService(d_authsvc);
Request authReq = authService.createAuthorizationRequest();
authReq.set("authId", authID);
authReq.set("ipAddress", appIP);
userIdentity = session.createIdentity();
authRequestID = new CorrelationID();
try
{
session.sendAuthorizationRequest(authReq, userIdentity, authRequestID);
}
catch (Exception e)
{
System.out.println("Unable to send authorization request: " + e.getMessage());
}
In the above code, you can see that an empty identity object is created using session.createIdentity(). This is the object that will be populated once successful authentication has been achieved, and it is the object that will need to be cached.
We will receive a Response event for the Authentication service. In the example below, we use a CorrelationID to identify messages from the Authentication service, and check for success or failure:-
if(msg.correlationID()==authRequestID) {
if(msg.messageType().equals(AUTHORIZATION_SUCCESS)) {
System.out.println("Authorised...Opening EMSX service...");
System.out.println("Seat Type: " + userIdentity.seatType().toString());
session.openServiceAsync(d_service);
} else if(msg.messageType().equals(AUTHORIZATION_FAILURE)) {
System.out.println("Authorisation failed...");
System.out.println(msg.toString());
wait(1000);
// Automatically retry...
sendAuthRequest(session);
} else {
System.out.println("Unexpected authorisation message...");
System.out.println(msg.toString());
}
}
When we receive the successful authorization, we can continue with opening the usual EMSX service. If multiple authorization requests have been sent, for a number of different UUIDs, it is necessary to wait for all the responses before being able to use all the identity objects.
In the above code, you will see that we examine the ‘seatType’ of the identity. The seat type in this case will be either BPS or non-BPS.
Using User Identities¶
When a client application connects to EMSX<GO> via the API on desktop, it does so by leveraging the identity of the logged in Bloomberg terminal user. This means that when a request or subscription object is received by the Bloomberg infrastructure, the target EMSX blotter can be identified.
In the server environment, there is no Bloomberg terminal, and therefore no implied user can be identified. Moreover, the server is capable of connecting to any number of EMSX user blotters, simultaneously. Therefore, the application making the call must indicate which user is the intended target. This is done through the creation and use of Identity object.
An Identity object represents a specific Bloomberg UUID. Once created, an Identity object can be cached for 24hrs, and used with every sendRequest() and subscribe() call.
Identity objects are live, that is they remain connected to Bloomberg in real-time and are capable of receiving events. We recommend that an identity is recreated every 24hrs, to ensure that it picks up the latest changes to any user settings, including access to EMSX.
Any number of user Identity object can be created by a server-side application. If the application uses the identities of real traders within a firm, then each trader would have an identity created to represent them in the server application. The server application would, perhaps, receive an instruction from the upstream client-side application to create an order in a trader’s blotter. The server application would select the appropriate user identity from the cache and add it to the request.
Migrating the existing desktop application call to a server application simply involves changing all sendRequest() and subscribe() calls to include the appropriate identity, as follows:-
DAPI:
session.sendRequest(request, requestID);
session.subscribe(subscriptions);
Server:
session.sendRequest(request, Identity, requestID);
session.subscribe(subscriptions, Identity);
Following python sample summarizes the above:-
import sys
import blpapi
import datetime
import time
SESSION_STARTED = blpapi.Name("SessionStarted")
SESSION_TERMINATED = blpapi.Name("SessionTerminated")
SESSION_STARTUP_FAILURE = blpapi.Name("SessionStartupFailure")
SESSION_CONNECTION_UP = blpapi.Name("SessionConnectionUp")
SESSION_CONNECTION_DOWN = blpapi.Name("SessionConnectionDown")
SERVICE_OPENED = blpapi.Name("ServiceOpened")
SERVICE_OPEN_FAILURE = blpapi.Name("ServiceOpenFailure")
SLOW_CONSUMER_WARNING = blpapi.Name("SlowConsumerWarning")
SLOW_CONSUMER_WARNING_CLEARED = blpapi.Name("SlowConsumerWarningCleared")
SUBSCRIPTION_FAILURE = blpapi.Name("SubscriptionFailure")
SUBSCRIPTION_STARTED = blpapi.Name("SubscriptionStarted")
SUBSCRIPTION_TERMINATED = blpapi.Name("SubscriptionTerminated")
AUTHORIZATION_SUCCESS = blpapi.Name("AuthorizationSuccess")
AUTHORIZATION_FAILURE = blpapi.Name("AuthorizationFailure")
HANDLE = blpapi.Name("handle")
#EMSX/IOI API Server authentication
d_service = "//blp/emapisvc_beta"
d_auth = "//blp/apiauth"
d_host = "1.2.3.4" #static ip address of the server
d_port = 8195
d_user = "MyAuthIDOrEMRSID"
.
.
.
class SessionEventHandler():
def sendAuthRequest(self, session):
authService = session.getService(d_auth)
authReq = authService.createAuthorizationRequest()
authReq.set("emrsId", d_user)
authReq.set("ipAddress", d_host)
self.identity = session.createIdentity ()
print("Sending authorization request: %s" % (authReq))
session.sendAuthorizationRequest(authReq, self.identity)
print("Authorization request.sent.")
.
.
.
def processSessionStatusEvent(self,event,session):
print("Processing SESSION_STATUS event")
for msg in event:
print(msg)
if msg.messageType() == SESSION_STARTED:
print("Session started...")
session.openServiceAsync(d_auth)
elif msg.messageType() == SESSION_STARTUP_FAILURE:
sys.stderr.write("Error: Session startup failed")
elif msg.messageType() == SESSION_CONNECTION_UP:
print("Session connection is up")
elif msg.messageType() == SESSION_CONNECTINO_DOWN:
print("Session connection is down")
else:
print(msg)
def processServiceStatusEvent(self,event,session):
print("Processing SERVICE_STATUS event")
for msg in event:
print(msg)
if msg.messageType() ==SERVICE_OPENED:
serviceName = msg.asElement().getElementAsString("serviceName");
print("Service opened [%s] % (serviceName))
if serviceName==d_auth;
print("Auth service opened... Opening application service...")
session.openServiceAsync(d_service)
elif serviceName==d_service;
print("Application service opened... Sending authorization request...")
self.sendAuthRequest(session)
elif msg.messageType() == SERVICE_OPEN_FAILURE:
print("Error: Service Failed to open")
def processAuthorizationStatusEvent(self,event):
print("Processing AUTHORIZATION_STATUS event")
for msg in event:
print("AUTHORIZATION_STATUS message: %s" % (msg))
.
.
.
Server Side Request/Response¶
As of today, the following emapisvc and emapisvc_beta requests are available from the server side access.
| Request Name | Action |
|---|---|
| AssignTrader | Assign an order to another UUID. |
| CancelRouteEx | Cancel outstanding routes (placements). |
| CreateOrder | Create an order or stage an order into EMSX<GO>. |
| CreateOrderAndRouteEx | Create a new order and route in a single request. |
| CreateOrderAndRouteManually | Create the order and notify EMSX this is routed. |
| DeleteOrder | Delete an existing order in EMSX<GO>. |
| GetAllFieldMetaData | Get all field meta data in a response message. |
| GetBrokerStrategiesWithAssetClass | Get all broker strategy information and asset class data. |
| GetBrokerStrategyInfoWithAssetClass | Get all broker strategy info and asset class data. |
| GetBrokerWithAssetClass | Get all broker data with asset class in a response message. |
| GetFieldMetaData | Get field meta data in a reponse message. |
| GetTeams | Get team data in a response message. |
| GroupRouteEx | Submit the entire list as a single route to a basket algorithm. |
| ModifyOrder | Modify parent order. |
| ModifyRouteEx | Modify child route. |
| RouteEx | Route existing order. |
| RouteManuallyEx | Route manually and notify EMSX that it is routed. |
Any other requests will return the following error:
"Obsolete request type: " << request_type